- Magnesium Mass Number And Atomic Number
- Magnesium Mass Number Rounded
- Magnesium Mass Number 25
- Magnesium Mass Number 24
This should allow them to calculate the mass of the mass of the magnesium (mass 2 – mass 1) and the mass of the product (mass 3 – mass 1). They could also calculate the increase in mass (mass 3 – mass 2), which corresponds to the mass of oxygen.
The isotope chart will show that there are three stable isotopes of magnesium: Mg-24, Mg-25, and Mg-26. The number is the mass number. It is the total number of protons and neutrons in the atom. Subtract the atomic number from the mass number and you get the number of neutrons. Natural magnesium is always a mixture of the three isotopes. There are mainly three Magnesium isotopes that are stable: Mg 24, 25 and 26. The abundance on earth of the first is 79% the second 10% and the third 11%. The relative atomic mass of Magnesium (the average of all the masses of the stable isotopes) is stated as 24.31 in most of the periodic tables and 24.305 in more specific references. Magnesium is a cofactor for at least 300 enzymes and is important for several functions in the body with some key processes identified below.A32810 Enzymes that rely on magnesium to operate help produce energy through oxidative phosphorylation, glycolysis and ATP metabolism.A39559 They are also involved in nerve function, muscle contraction.
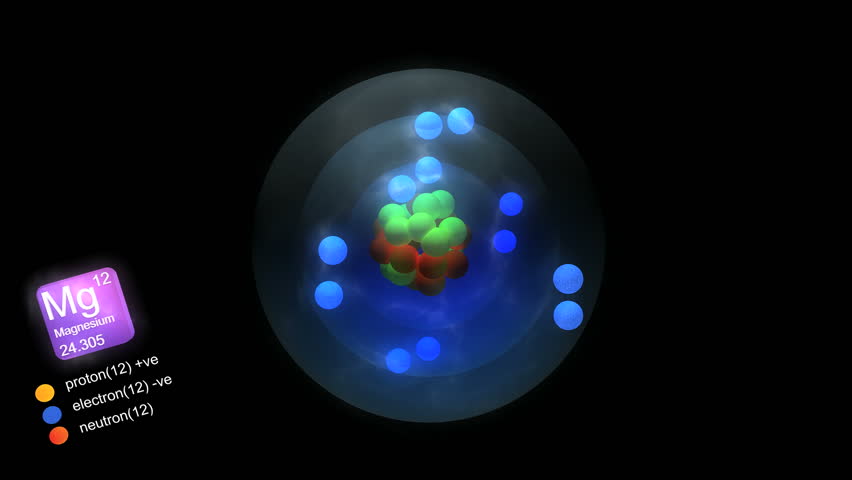
Atomic Number of Magnesium is 12.
Chemical symbol for Magnesium is Mg. Number of protons in Magnesium is 12. Atomic weight of Magnesium is 24.305 u or g/mol. Melting point of Magnesium is 648,8 °C and its the boiling point is 1107 °C.
» Boiling Point» Melting Point» Abundant» State at STP» Discovery Year
About Magnesium
Magnesium is a soft metal of light grey color, which can easily burn with bright fire. Magnesium is an essential element for all living things on our planet since a molecule of magnesium is in every cell of chlorophyll, which is the material for photosynthesis. In human body, magnesium is a compound of various enzymes necessary for correct and smooth chemical reactions in our body tissues. Since magnesium is very highly reactive, it can’t be found freely in nature, but it can be obtained from a number of natural sources, manly such minerals as dolomites, magnesites, etc. It is the 8th most abundant element on our planet. It has a variety of uses, primarily as a light but relatively strong metal, especially valuable for producing various consumers’ goods like suitcases, chairs, laptops, etc. Magnesium and its compounds are used to produce fireworks, as well as in medicine (especially for producing spasms reducing medicines, as laxatives, etc.).
Uses of Magnesium
Magnesium (Mg) is the most commonly used structural metal after iron and aluminum. It is especially used in the production of steel and iron to remove sulfur as well as one of the most important construction metals in aircraft and automotive industry. Magnesium is widely used in making mobile phones, cameras, televisions, tablet computers, and laptops.
Its compounds are mostly used in construction, electronics, medicine, and sports. For example, Magnesium chloride, the chemical compound with the formula MgCl2 is used for dust control and ice control. This compound is also used in nutraceutical and pharmaceutical preparations too. It is preferred in the preparation of tofu from soy milk as a coagulant. Magnesium sulfite is used in the producing of paper. Besides, magnesium alloys are very important in the airplane and car construction.
There are some other usages of magnesium as a reducing agent and an additive agent in various industries.
Magnesium is also very important for our body. It helps to convert food into energy, repair DNA and RNA, plays an important role in brain functions, and helps to prevent migraine headaches.
Compounds with Magnesium
- MgCl2: Magnesium chloride
- MgO: Magnesium oxide
- Mg(OH)2: Magnesium hydroxide
- MgSO4: Magnesium sulfate
- MgCO3: Magnesium carbonate
- MgSO3: Magnesium sulfite
- F6MgSi: Magnesium hexafluorosilicate
- MgB2: Magnesium diboride
- MgBr2: Magnesium bromide
- MgC2O4: Magnesium oxalate
- MgF2: Magnesium fluoride
Properties of Magnesium Element
| Atomic Number (Z) | 12 |
|---|---|
| Atomic Symbol | Mg |
| Group | 2 |
| Period | 3 |
| Atomic Weight | 24.305 u |
| Density | 1.738 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point (K) | 923 K |
| Melting Point (℃) | 648,8 °C |
| Boiling Point (K) | 1363 K |
| Boiling Point (℃) | 1107 °C |
| Heat Capacity | 1.023 J/g · K |
| Abundance | 23300 mg/kg |
| State at STP | Solid |
| Occurrence | Primordial |
| Description | Alkaline earth metal |
| Electronegativity (Pauling) χ | 1.31 |
| Ionization Energy (eV) | 7.64624 |
| Atomic Radius | 150pm |
| Covalent Radius | 130pm |
| Van der Waals Radius | 173 |
| Valence Electrons | 2 |
| Year of Discovery | 1755 |
| Discoverer | Black |
What is the Boiling Point of Magnesium?
Magnesium boiling point is 1107 °C. Boiling point of Magnesium in Kelvin is 1363 K.
What is the Melting Point of Magnesium?
Magnesium melting point is 648,8 °C. Melting point of Magnesium in Kelvin is 923 K.

How Abundant is Magnesium?
Magnesium Mass Number And Atomic Number
Pokemon infinite fusion. Abundant value of Magnesium is 23300 mg/kg.
What is the State of Magnesium at Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP)?
Magnesium Mass Number Rounded
State of Magnesium is Solid at standard temperature and pressure at 0℃ and one atmosphere pressure.

When was Magnesium Discovered?
Magnesium Mass Number 25
Magnesium was discovered in 1755.
Magnesium Mass Number 24
